Selection is one of the most important HR tasks for an
organization as it is vital to fill the vacant job positions not only with suitably
skilled people but also should be more flexible and should be willing and able
to cope with the change (Leatherbarrow & Fletcher, 2015).
Selecting the most suitable candidate for the job position
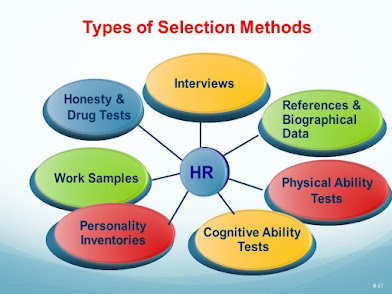
can be done using application evaluation, written tests, interviews, background
tests, and medical tests. Most organizations use the application evaluation
method as the first selection method (Chandrashekar & Sahin, 2014). However,
through this mostly interpersonal skills and personality traits would not be
encountered and only the paper qualification and job experience would be
considered. Therefore, sometimes more qualified and suitable candidates would
be ignored through this process. The process of selection more importantly
should be unbiased and comply with the relevant legal and regulatory frameworks
of the organization and the Human resource department should look through wider
corporate requirements (Armstrong & Taylor, 2014).
|
Figure 1 - Selection Methods |
Source:(Chandrashekar & Sahin, 2014)
The most common method of employee selection involves individual
interviews which are mostly conducted by the hiring managers or HR
representatives of the organization. Some hiring managers plan a structured
interview process with a planned question series with scoring metrics
beforehand and some prefer to build up a rapport with the employee based on
their responses to the initial questions shared. If one interviewer is involved
in this process, there could be biased or superficial decisions and to avoid
this most organizations use an interview process consisting of several stages
or interview panel (Armstrong, 2014).
The company which I work for mainly uses this method in the
selection process in which the relevant department heads and some skilled
interviewers are involved for technical considerations and sorted employees
will go through an interview conducted by the Human Resource division.
Assessing the behavior knowledge and ability of the
candidates is quite often used selection method. These types of tests should be
used with proven validity and for this employers use different validity
criteria. For the selection test to be useful, it is necessary that the test is
related and has a predictable result for the performance of the future
employee. In common practice, several types of tests are used, such as
intelligence tests (IQ and EQ), abilities tests (thinking, behaviors),
personality tests (types), and vocational tests (Goleman, 2011).
Intelligence tests mostly involve measuring a set of mental
abilities and capabilities to handle a certain task that needs abstract
thinking and reasoning. These types of tests are concerned with general
intelligence and are therefore called general mental ability (GMA) tests
(Armstrong, 2010).
According to Armstrong (2010) ability tests involves Verbal reasoning, Numerical reasoning, Spatial reasoning, and Mechanical reasoning. Verbal reasoning measures the ability to comprehend, interpret and draw conclusions from oral or written language while Numerical reasoning measures the ability to comprehend numerical information. Spatial reasoning assesses the ability to understand and interpret spatial relations between objects and mechanical reasoning measures the understanding of physical laws.
Aptitude tests are tests that are designed to assess the capability of carrying out a task specific to the job which predicts the performance of the employee. Many contemporary organizations like Ceylon Electricity Board, and Airport Aviation in Sri Lanka use this method as a selection criterion in the process of hiring employees for the organization.
There is no best selection method in which it is possible to
immediately and accurately know the job applicant. Therefore, it is appropriate
to combine more methods and obtain an accurate profile in order to find the
most suitable candidate, find motivation, and the reason why the candidate is
interested in a particular job (Vetráková et al., 2011).
References
Armstrong, M. (2010). Armstrong's essential human resource management practice. London: Kogan Page.
Armstrong, M., and Taylor, S., (2014) Armstrong’s handbook of human resource management practice. (13th Ed) London: Kogan Page
Chandrashekar, G. and Sahin, F., (2014). A survey on feature selection methods. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 40(1), pp. 16-28.
GOLEMAN, D. 2011. Emoční inteligence. Praha : Metafora, 336 p.
Leatherbarrow, C., Fletcher, J. (2015). Introduction to Human Resource Management: A Guide to HR in practice, 3rd Edition, London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development.
Very informative and insightful article! According to Bibi et al. (2021), the presence of nepotism and favoritism during the execution of recruitment selection has now become a major concern for both developed and developing countries. However, adopting the techniques that you have discussed above would get rid of the organizational politics during recruitment and selection, allowing the organization to acquire a more qualified workforce.
ReplyDeleteThanks Uditha for your valuable comment. The importance of having efficient and effective procedures for recruitment and selection can hardly be exaggerated. Cole (2002) is of the view that when organizations are able to find and employ qualified employees who are consequently able to fit in their roles and are competent, the organization will be able to take advantage of opportunities and take care of threats and competition from its operating environments that other organizations who are constantly battling with building and maintaining their workforce.
Delete